Attacks
Attacks
Vehicle platooning relies heavily on sensors
such as cameras and GPS as well as capabilities such as vehicle to
vehicle communication (V2V) and a 3G/4G connectivity. These sensors
could be tampered with, making the platoon vulnerable to attacks. In
addition, wireless communication signals can be intercepted and false
data can be projected back to the victim. Vehicles use wireless
communication to send information such as their speed, position and
acceleration to other vehicles in the platoon, who then, use this
information to adjust their speed accordingly. If a hacker was to
intercept this communication and then manipulate the data and
rebroadcast it to other vehicles in the platoon, the consequences would
be severe. A hacker could cause crashes, reduce fuel economy (by
constantly manipulating vehicles into changing their acceleration),
break a platoon up, or cause vehicles to not reach their final
destination (by intercepting and/or manipulating GPS data).
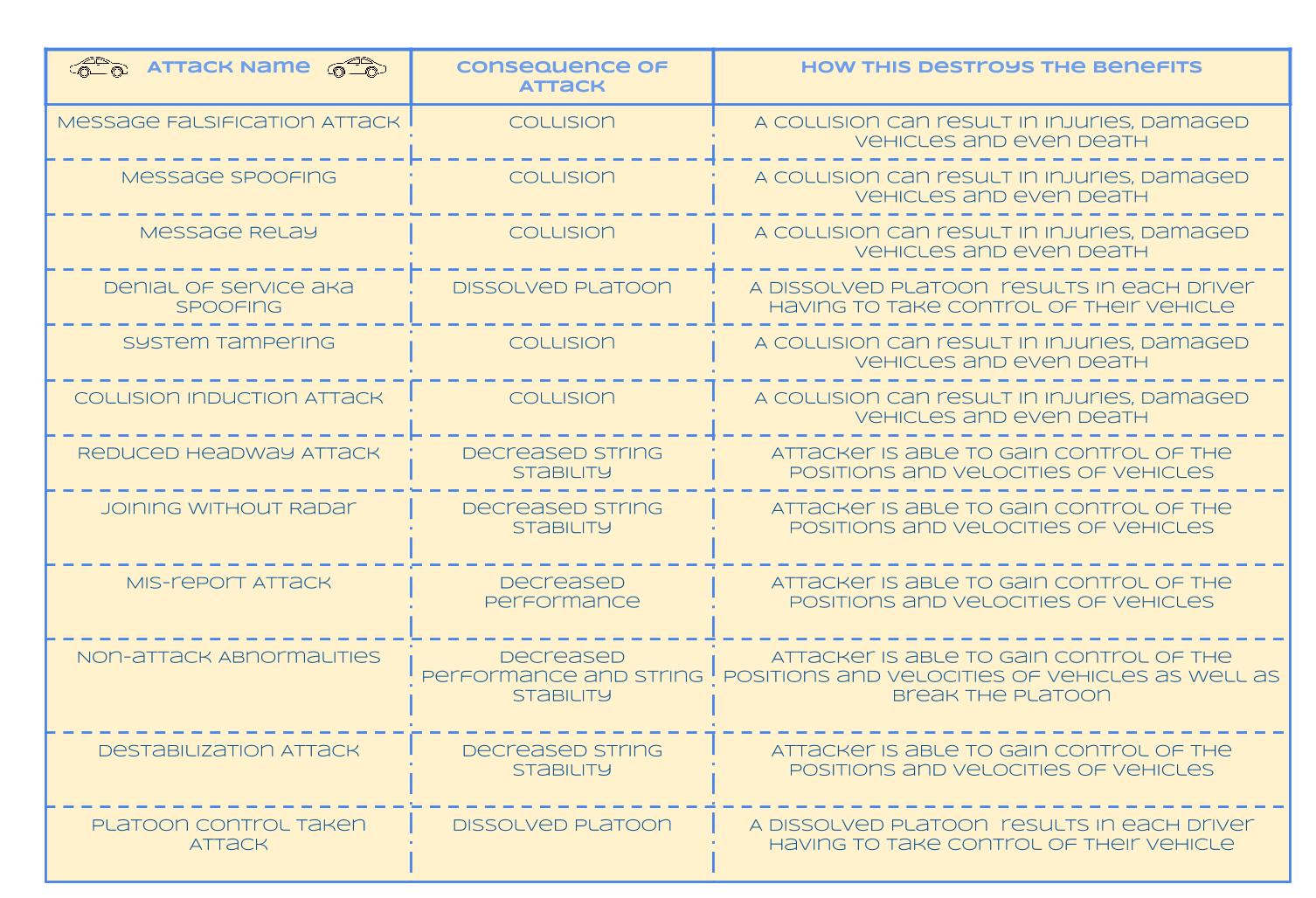
Application Layer Attacks:
Application layer attacks affect the functionality of a particular application such as CACC beaconing or message exchange in the platoon management protocol. The adversary can use message falsification, spoofing or replay attacks to maliciously affect the vehicle stream.
Network Layer Attacks:
Unlike application layer attacks, network layer attacks have the potential to affect the functioning of multiple user applications. For instance, the adversary can attempt a denial-of-service(DoS) or distributed DoS (DDoS) attack to overwhelm the communication capability of a vehicle.
System Level Attacks:
All presented attacks so far have been centered around exploiting V2V communication. Another type of attack is tampering with vehicle hardware or software, which can be done by malicious insider at the manufacturing level or by an outsider in an unattended vehicle.
Privacy Leakage Attacks:
CACC vehicles periodically broadcast beacons that contain various types of information such as vehicle identity, current vehicle position, speed and acceleration
The adversary can carry out an eavesdropping attack to extract valuable information about the vehicle stream